Hepatitis E (HEV) is a viral infection that can have serious consequences, especially for pregnant women. The virus is primarily spread through contaminated water or food and can cause liver damage and even death.
One of the most concerning aspects of hepatitis E during pregnancy is that it can lead to a higher maternal and fetal mortality risk.
Pregnant women are more likely to experience severe symptoms and complications from HEV infection, and the virus can also harm the developing fetus.
According to World Health Organization, hepatitis E in pregnancy third trimester can be fatal for around 20–25% of pregnant women.
So, what can you do to protect yourself and your baby from hepatitis E during pregnancy?
Scroll down for the answers.
Let us start with an overview of hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is a viral infection that attacks the liver and causes inflammation. It is primarily spread through contaminated water or food and can lead to severe symptoms such as jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
It can be dangerous for pregnant women and can result in liver failure. Nonetheless, it is preventable through proper sanitation and safe food handling practices.
Remember that early diagnosis and treatment can make a big difference in the outcome of the infection.
Dr. Mohit Saraogi, an experienced obstetrician and IVF specialist in Mumbai, says, “It is important to take precautions and be vigilant in order to protect yourself and your baby from hepatitis E. With the right knowledge and preventive measures, you can keep yourself and your baby safe during pregnancy.”
If you feel you have contracted the disease, do not waste time and consult your gynecologist immediately. It is better to be safe than sorry.
You can consult Dr. Mohit Saraogi at Saraogi Hospital in Mumbai for safe and effective hepatitis E in pregnancy treatment.
Check out the causes and symptoms that can help you be vigilant.
What are the causes of hepatitis E in pregnancy?
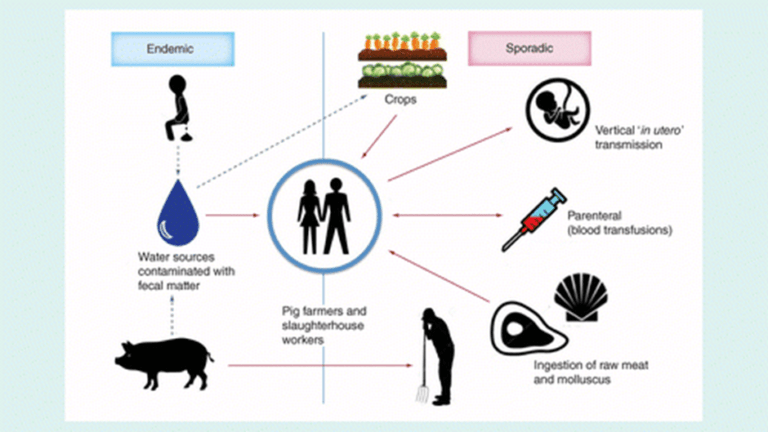
Some common causes of hepatitis E are as follows:
- Consumption of contaminated water or food
- Poor hygiene practices
- Coming into contact with HEV-infected fecal matter
- Consuming raw or undercooked meat, such as pork
- Living in or traveling to areas with poor sanitation or high rates of HEV infection
- Having a weakened immune system
What are the symptoms of hepatitis E in pregnancy?
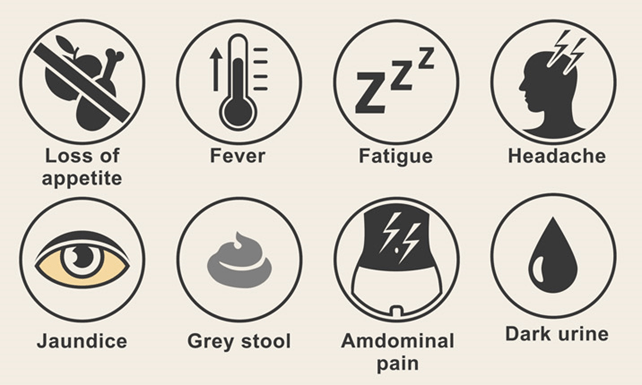
Hepatitis E and pregnancy together can cause severe complications. If you experience any of the symptoms below, seek immediate medical attention.
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Itchy skin
- Clay-colored stool
- Flu-like symptoms (such as fever, headache, and muscle aches)
Please note that some pregnant women with HEV infection may not have any symptoms at all or may have very mild symptoms.
Now, let’s understand hepatitis E in pregnancy treatment options.
Treatment for hepatitis E in pregnancy is primarily focused on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
The hepatitis E virus usually clears up on its own within a few weeks, but in some cases, it can lead to severe complications, especially for pregnant women.
Here are some treatment options for hepatitis E in pregnancy:
Rest: Pregnant women with HEV infection should rest as much as possible and avoid strenuous activity to help the body fight the infection.
Supportive care: They should drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration and consume a balanced diet.
Medications: In some cases, the doctor may give pregnant women with HEV infection medications to help manage symptoms or prevent complications.
Monitoring: They will be closely monitored by their obstetrician to check for signs of complications and to ensure the health of the mother and the baby.
Hospitalization: In severe cases of HEV infection, the women may need to be hospitalized to receive more intensive treatment and monitoring.
As of now, there is no specific treatment for hepatitis E, but early diagnosis and treatment can help in the outcome of the infection.
Also, there is no vaccine available for general use, so the best way to prevent hepatitis E is to practice good hygiene and make sure only to consume clean water and properly cooked food.
What happens if you have hepatitis E during pregnancy?
Hepatitis E during pregnancy can have severe consequences for both the mother and the developing fetus
For the mother, HEV infection can cause symptoms such as fatigue, stomach pain, jaundice, and dark urine.
The infection can sometimes lead to liver failure and even death, particularly in people with weakened immune systems or pre-existing liver conditions.
For the fetus, HEV infection can lead to several complications, such as:
Fetal growth restriction: The virus can reduce the growth of the fetus, leading to lower birth weight.
Premature birth: It can lead to early delivery of the baby.
Miscarriage: Sometimes, hepatitis E during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage.
Stillbirth: In rare cases, it can lead to stillbirth.
The above complications are relatively rare, and most women infected with hepatitis E during pregnancy will have a full-term pregnancy with a healthy baby.
However, it is crucial for pregnant women who have been exposed to the virus or are experiencing symptoms to seek medical attention right away to minimize the risk of complications.
What are the risk factors for hepatitis E in pregnancy?

The risk factors for hepatitis E in pregnancy are similar to those for the general population and include the following:
- Living in or travelling to areas with poor sanitation or high rates of hepatitis E
- Consuming contaminated water or food.
- Following poor hygiene, like not washing hands regularly or not correctly cleaning fruits and vegetables.
- Having a weakened immune system, like those who have HIV or other chronic illnesses.
- Eating raw or undercooked meat, such as pork.
- Occupational exposure to HEV-contaminated animal feces.
Recovery time
The recovery time for Hepatitis E can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection.
Dr. Mohit Saraogi states, “In most cases, the infection will clear up on its own within a few weeks, but in some cases, it can develop into serious complications, especially for pregnant women. Close monitoring is needed to ensure the health of the mother and the baby.”
During recovery, the infected person needs to rest, practice good hygiene, maintain a healthy diet, and stay hydrated. Your doctor may prescribe medications to manage symptoms.
Ways to prevent hepatitis E in pregnancy
Practice good hygiene: This includes washing your hands regularly and ensuring you only consume clean water and properly cooked food.
Be aware of the symptoms: If you experience any of the symptoms of hepatitis E, consult your doctor immediately.
Seek medical attention: If you are pregnant and have been exposed to the virus or are experiencing symptoms, seek medical attention right away.
Conclusion
Dr. Mohit Saraogi, a fertility specialist at Saraogi Hospital, a premier IVF centre in Mumbai, emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and treatment for pregnant women with hepatitis E to minimize the risk of complications.
You can schedule an appointment with Dr. Mohit Saraogi, who has the knowledge and experience to provide the best care and guidance for all gynecological and fertility issues and conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why hepatitis E is common in pregnancy?
Hepatitis E is a virus that is spread mainly through contaminated water. It is more common in pregnant women because their immune systems are weakened during pregnancy, making them more vulnerable to infection.
Why hepatitis E is fatal in pregnancy?
Hepatitis E is typically a mild disease, but it can be fatal in pregnant women because the virus can cause severe liver damage and increase the risk of developing jaundice and other complications.
Furthermore, pregnant women have a weakened immune system, which makes them more susceptible to severe illness from the virus. The virus also causes a greater risk of miscarriage and stillbirth.

